 ;
;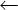 .
.| Wily Hacker's Problem |
Wily Hacker finds on his chief's desk the encryption scheme of the chief's most important messages. He also finds, in his chief's computer, files with cryptograms and the associated encryption keys. He wishes to write a program for decrypting these cryptograms.
Wily read a book about modern encryption. He discovered that twenty years ago cryptography became the subject of many applications in the domain of computer data security. More and more persons wish to make their messages and files confidential. A cipher is a secret method of transforming plaintext (message) into ciphertext (cryptogram). This operation, called encryption, is controlled by an encryption key. There must exist the reverse transformation, called decryption, which transforms ciphertext into plaintext using a decryption key, which is derived using the encryption key.
Wily observes that the algorithm shown in the figure encrypts the 64-bit message M into the 64-bit cryptogram C, under the control of the 64-bit key K.
The encryption function uses 3 types of operations:
 ;
;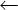 .
.The algorithm uses the following notations:
Your task is to write a program that obtains plain messages from cryptograms and decryption keys by discovering a suitable scheme, just like Wily Hacker did.
85bfa0242caa796e 1111222233334444 4c0d17279cbf4222 abcdabcdabcdabcd
TEACHERS STUDENTS