Interpreting SQL
Time limit: ? seconds
Memory limit: 64 megabytes
Your task is to write the part of the SQL server YourSQL
responsible for processing queries.
Your server manages a relational database consisting of
several tables. Each table has rows and columns; each column
has a fixed type (number or string) and a name. Each cell of
the table also has a type, which is equal to the type of its
column. No two different columns of a table have the same
name. Tables also have distinct names.
Here is a sample table (the upper row contains column names;
string cells are aligned to the left, numeric to the right):
| Account |
LastName |
FirstName |
Balance |
| 1 | Ivanov | Petr | 2500 |
| 2 | Petrov | Ivan | 2000 |
| 3 | Ivanov | Ivan | 3000 |
An SQL query is a string telling the server to get
some or all of data from one or more tables, form it up into
a temporary table and transfer it to the client (after that,
the temporary table is destroyed). Here is the YourSQL query
syntax:
query ::= `SELECT' select `FROM' from possible-where possible-order;
select ::= `*' | column-list;
column-list ::= name | name `,' column-list;
from ::= name | inner-from `INNER' `JOIN' inner-from `ON' name `=' name;
inner-from ::= name | `(' inner-from `INNER' `JOIN' inner-from `ON' name `=' name `)';
possible-where ::= empty | `WHERE' where;
where ::= where-2 | where-2 (`AND' | `OR') where;
where-2 ::= `(' where `)' | `NOT' where-2 | value operation value;
operation ::= `=' | `<' | `>' | `<=' | `>=' | `<>';
value ::= number | string-constant | name;
possible-order ::= empty | `ORDER' `BY' order-by;
order-by ::= order-column | order-column `,' order-by;
order-column ::= name (empty | `ASCENDING' | `DESCENDING');
empty ::= ;
number ::= (empty | `+' | `-') . unsigned;
unsigned ::= digit | digit . unsigned;
digit ::= `0' | `1' | `2' | `3' | `4' | `5' | `6' | `7' | `8' | `9';
name ::= letter | name . (letter | digit);
letter ::= `a' | `b' | `c' | `d' | `e' | `f' | `g' | `h' | `i' | `j' | `k' | `l' | `m'
| `n' | `o' | `p' | `q' | `r' | `s' | `t' | `u' | `v' | `w' | `x' | `y' | `z'
| `A' | `B' | `C' | `D' | `E' | `F' | `G' | `H' | `I' | `J' | `K' | `L' | `M'
| `N' | `O' | `P' | `Q' | `R' | `S' | `T' | `U' | `V' | `W' | `X' | `Y' | `Z';
string-constant ::= `"' . escaped-string . `"';
escaped-string ::= empty | escaped-symbol . escaped-string;
escaped-symbol ::= digit | letter | special-symbol | other-symbol;
special-symbol ::= `\\' | `\"';
other-symbol ::= `!' | `#' | `$' | `%' | `&' | `'' | `(' | `)' | `*' | `+' | `,' | `-'
| `.' | `/' | `:' | `;' | `<' | `=' | `>' | `?' | `@' | `[' | `]' | `^' | `_' | ``' | `{' | `|' | `}'} | `~';
The period (.) between two subsequent terms means that there
may be no spaces between these terms. If there is no period
between two terms, then they may be separated by any amount
of spaces, tab characters and carriage returns; two names
that are not separated by a period will be separated by at
least one space, tab character or carriage return.
Parenthesis are used to group terms. There is no difference
between uppercase and lowercase letters except in string
constants.
The query is executed the following way:
- The search table is made from the `FROM ...' part of
the query. If the `FROM ...' statement contains only one
name, then this name is the name of the search table.
Otherwise the from statement is `from1 INNER JOIN
from2 ON name1=name2', where from1 and from2
are from statements; tables table1 and table2 must be
made from from1 and from2 respectively before making
the search table. In this case, name1 and name2 are
the names of some columns in table1 and table2
respectively; these two columns are of the same type. The
list of the search table's columns is the list of the
table1 columns followed by the list of the table2
columns. (It is guaranteed that no two columns in table1
and in table2 have the same names.) The search table's
rows are obtained in the following way. First, a row list
(row 1 of table1+row 1 of table2), (row 1 of
table1+row 2 of table2), \dots, (row 2 of
table1+row 1 of table2) is made (here `+' means row
concatenation). Then the rows from the list which have the
values of the columns name1 and name2 equal are
selected from this list to form the search table; the order
of the rows remains the same.
For example, if table1 is the table above and table2
is
| From | To | Amount |
| 1 | 2 | 1000 |
| 2 | 3 | 2000 |
| 3 | 1 | 3000 |
| 2 | 1 | 10 |
then the result of `from1 INNER JOIN from2 ON Account=From' will be
| Account | LastName | FirstName | Balance |
From | To | Amount |
| 1 | Ivanov | Petr | 2500 | 1 | 2 | 1000 |
| 2 | Petrov | Ivan | 2000 | 2 | 3 | 2000 |
| 2 | Petrov | Ivan | 2000 | 2 | 1 | 10 |
| 3 | Ivanov | Ivan | 3000 | 3 | 1 | 3000 |
- The rows are selected from the search table to form
the result table. If there is no WHERE clause, all the rows
are selected. Otherwise the rows that satisfy the WHERE
clause are selected. Sequences
\\ and
\" are treated as \ and
" respectively in escaped strings. All logical
and comparison operations have their usual meaning; strings
are compared lexicographically; compared values will always
be of same type. The operations are executed from left to
right; i.e., `a AND b OR c' means `(a AND b) OR c'. The
names in the WHERE clause are the names of the columns of
the table.
- The rows of the result table are ordered. If there is
an ORDER BY clause, the rows are ordered by the first column
in the clause; the rows with equal first column value are
ordered by the second column etc. The strings are ordered
lexicographically. The ASCENDING or DESCENDING word after
the column name represent the direction of the order:
ASCENDING means that the smallest row will be first and
DESCENDING means that the smallest row will be last. The
ASCENDING direction is default. The sorting is stable, i.e.,
the order of equivalent rows remains the same.
- The columns which will be output will be selected. If
an asterisk follows the SELECT word, then all the columns
are selected. Otherwise the list of the selected columns is
given after the SELECT word; the columns are outputted in
the given order. (Note: the column list after the SELECT
word may contain the same column more than one time; in this
case, the column is outputted each time it appears in the
list).
Input
The first line of the input contains the number of the
test cases, which is at most 35. The descriptions of the
test cases follow.
The first line of a test case description contains a single integer
K (1 ≤ K ≤ 20), denoting the number of tables. The
table descriptions follow. The first line of a table
description is the name of the table followed by two
integers, M and N (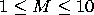 ,
, 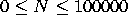 ), which are the number of columns and the number of
rows respectivelty. Each of the next M lines contains the
name of a row and its type (
), which are the number of columns and the number of
rows respectivelty. Each of the next M lines contains the
name of a row and its type (S for string, I for
numeric). Each of the next N lines contains M strings or
integers, being the table data. The i-th line contains
data for row i. The strings and the numbers in the input
tables are separated by spaces; the strings are not escaped.
The rest of the input file contains the query.
The numbers in the input may not exceed 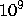 by absolute
value and do not have leading zeroes; the strings are of
length no more than 100, the length of the names does not
exceed 20. The overall number of cells in all the input tables
does not exceed 100000; the overall number of string cells in
all the input tables does not exceed 10000. There are no more
than 10 INNER JOIN statements. In each joining operation,
the product of the number of rows in the first table and
the number of rows in the second table does not exceed 10000;
the product of the previous number and the sum of the number
of columns of the two tables does not exceed 100000. The
search table contains at most 100000 cells; at most 10000 of
them may be strings. If there is a WHERE clause, the search
table has at most 1000 rows. The length of the WHERE clause
(excluding the word `WHERE') does not exceed 400. There are
at most five columns in the ORDER BY clause. If the SELECT
word is followed by a column list, then this list contains
at most 10 columns and the product of the amount of the
columns in the list and the number of rows in the result table
does not exceed 10000.
by absolute
value and do not have leading zeroes; the strings are of
length no more than 100, the length of the names does not
exceed 20. The overall number of cells in all the input tables
does not exceed 100000; the overall number of string cells in
all the input tables does not exceed 10000. There are no more
than 10 INNER JOIN statements. In each joining operation,
the product of the number of rows in the first table and
the number of rows in the second table does not exceed 10000;
the product of the previous number and the sum of the number
of columns of the two tables does not exceed 100000. The
search table contains at most 100000 cells; at most 10000 of
them may be strings. If there is a WHERE clause, the search
table has at most 1000 rows. The length of the WHERE clause
(excluding the word `WHERE') does not exceed 400. There are
at most five columns in the ORDER BY clause. If the SELECT
word is followed by a column list, then this list contains
at most 10 columns and the product of the amount of the
columns in the list and the number of rows in the result table
does not exceed 10000.
Output
For each test case in the input,
output the result table in the same
format as the tables in the input without the table name and
type specifications (see sample output). Note that there is
only one correct order of the columns and the rows of the
resulting table (see the rules above). Output the column names
in the same case that they were in the input. Output a blank line
between test cases.
Examples
| Input | Output |
1
2
AccountInfo 4 3
Account I
LastName S
FirstName S
Balance I
1 Ivanov Petr 2500
2 Petrov Ivan 2000
3 Ivanov Ivan 3000
AccountTransfers 3 4
From I
To I
Amount I
1 2 1000
2 3 2000
3 1 3000
2 1 10
SELECT LastName, FirstName, To, Amount
FROM AccountInfo
INNER JOIN AccountTransfers ON Account=From
WHERE FirstName<>"Petr"
ORDER BY LastName DESCENDING, Amount
|
4 3
LastName
FirstName
To
Amount
Petrov Ivan 1 10
Petrov Ivan 3 2000
Ivanov Ivan 1 3000
|